Sign-in
In order for IdentityServer to issue tokens on behalf of a user, that user must sign-in to IdentityServer.
Cookie authentication
Authentication is tracked with a cookie managed by the cookie authentication handler from ASP.NET Core.
IdentityServer registers two cookie handlers (one for the authentication session and one for temporary external cookies). These are used by default and you can get their
names from the IdentityServerConstants class (DefaultCookieAuthenticationScheme and ExternalCookieAuthenticationScheme) if you want to reference them manually.
Only the basic settings are exposed for these cookies (expiration and sliding), but you can register your own cookie handlers if you need more control.
IdentityServer uses whichever cookie handler matches the DefaultAuthenticateScheme as configured on the AuthenticationOptions when using AddAuthentication from ASP.NET Core.
Note
In addition to the authentication cookie, IdentityServer will issue an additional cookie which defaults to the name “idsrv.session”. This cookie is derived from the main authentication cookie, and it used for the check session endpoint for browser-based JavaScript clients at signout time. It is kept in sync with the authentication cookie, and is removed when the user signs out.
Overriding cookie handler configuration
If you wish to use your own cookie authentication handler, then you must configure it yourself.
This must be done in ConfigureServices after registering IdentityServer in DI (with AddIdentityServer).
For example:
services.AddIdentityServer()
.AddInMemoryClients(Clients.Get())
.AddInMemoryIdentityResources(Resources.GetIdentityResources())
.AddInMemoryApiResources(Resources.GetApiResources())
.AddDeveloperSigningCredential()
.AddTestUsers(TestUsers.Users);
services.AddAuthentication("MyCookie")
.AddCookie("MyCookie", options =>
{
options.ExpireTimeSpan = ...;
});
Note
IdentityServer internally calls both AddAuthentication and AddCookie with a custom scheme (via the constant IdentityServerConstants.DefaultCookieAuthenticationScheme), so to override them you must make the same calls after AddIdentityServer.
Login User Interface and Identity Management System
IdentityServer does not provide any user-interface or user database for user authentication.
These are things you are expected to provide or develop yourself.
If you need a starting point for a basic UI (login, logout, consent and manage grants),
you can use our quickstart UI.
The quickstart UI authenticates users against an in-memory database. You would replace those bits with access to your real user store.
We have samples that use ASP.NET Identity.
Login Workflow
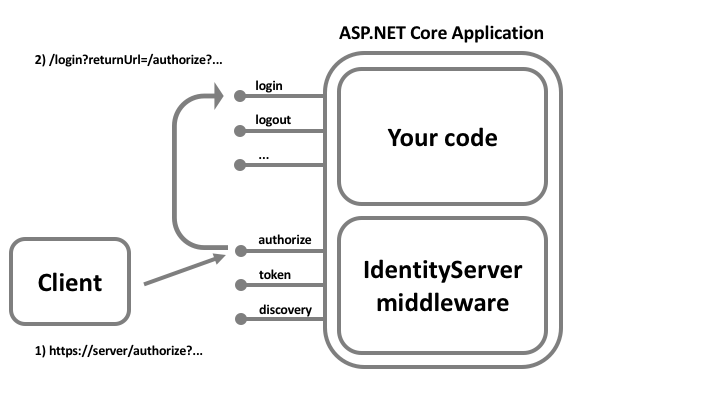
When IdentityServer receives a request at the authorization endpoint and the user is not authenticated, the user will be redirected to the configured login page.
You must inform IdentityServer of the path to your login page via the UserInteraction settings on the options (the default is /account/login).
A returnUrl parameter will be passed informing your login page where the user should be redirected once login is complete.
Note
Beware open-redirect attacks via the returnUrl parameter. You should validate that the returnUrl refers to well-known location. See the interaction service for APIs to validate the returnUrl parameter.
Login Context
On your login page you might require information about the context of the request in order to customize the login experience
(such as client, prompt parameter, IdP hint, or something else).
This is made available via the GetAuthorizationContextAsync API on the interaction service.
Issuing a cookie and Claims
There are authentication-related extension methods on the HttpContext from ASP.NET Core to issue the authentication cookie and sign a user in.
The authentication scheme used must match the cookie handler you are using (see above).
When you sign the user in you must issue at least a sub claim and a name claim.
IdentityServer also provides a few SignInAsync extension methods on the HttpContext to make this more convenient.
You can also optionally issue an idp claim (for the identity provider name), an amr claim (for the authentication method used), and/or an auth_time claim (for the epoch time a user authenticated).
If you do not provide these, then IdentityServer will provide default values.
